MediaCodec是Android提供的用于对音视频进行编解码的类,是Android Media基础框架的一部分,一般和 MediaExtractor, MediaMuxer, Surface和AudioTrack 一起使用。
MediaCodec的编解码流程MediaCodec采用异步方式处理数据,并且使用了一组输入输出buffer(ByteBuffer)。
1.使用者从MediaCodec请求一个空的输入buffer(ByteBuffer),填充满数据后将它传递给MediaCodec处理。 2.MediaCodec处理完这些数据并将处理结果输出至一个空的输出buffer(ByteBuffer)中。 3.使用者从MediaCodec获取输出buffer的数据,消耗掉里面的数据,使用完输出buffer的数据之后,将其释放回编解码器。
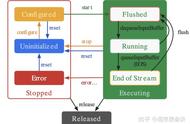
流程如下图所示:

MediaCodec的生命周期有三种状态:Stopped、Executing、Released。
Stopped,包含三种子状态:Uninitialized、Configured、Error。 Executing,包含三种子状态:Flushed、Running、End-of-Stream。

【相关学习资料推荐,点击下方链接免费报名,先码住不迷路~】
C 音视频配套学习资料:点击莬费领取→
Stopped的三种子状态: Uninitialized:当创建了一个MediaCodec对象,此时处于Uninitialized状态。可以在任何状态调用reset()方法使MediaCodec返回到Uninitialized状态。
Configured:使用configure(…)方法对MediaCodec进行配置转为Configured状态。
Error:MediaCodec遇到错误时进入Error状态。错误可能是在队列操作时返回的错误或者异常导致的。
Executing的三种子状态: Flushed:在调用start()方法后MediaCodec立即进入Flushed子状态,此时MediaCodec会拥有所有的缓存。可以在Executing状态的任何时候通过调用flush()方法返回到Flushed子状态。
Running:一旦第一个输入缓存(input buffer)被移出队列,MediaCodec就转入Running子状态,这种状态占据了MediaCodec的大部分生命周期。通过调用stop()方法转移到Uninitialized状态。
End-of-Stream:将一个带有end-of-stream标记的输入buffer入队列时,MediaCodec将转入End-of-Stream子状态。在这种状态下,MediaCodec不再接收之后的输入buffer,但它仍然产生输出buffer直到end-of-stream标记输出。
Released 当使用完MediaCodec后,必须调用release()方法释放其资源。调用 release()方法进入最终的Released状态。
主要API介绍简介:1.MediaCodec创建: createDecoderByType/createEncoderByType:根据特定MIME类型(如"video/avc")创建codec。 createByCodecName:知道组件的确切名称(如OMX.google.mp3.decoder)的时候,根据组件名创建codec。使用MediaCodecList可以获取组件的名称。
2.configure:配置解码器或者编码器。 3.start:成功配置组件后调用start。
4.buffer处理的接口: dequeueInputBuffer:从输入流队列中取数据进行编码操作。 queueInputBuffer:输入流入队列。 dequeueOutputBuffer:从输出队列中取出编码操作之后的数据。 releaseOutputBuffer:处理完成,释放ByteBuffer数据。
5.flush:清空的输入和输出端口。 6.stop:终止decode/encode会话 7.release:释放编解码器实例使用的资源。
MediaCodec创建MediaCodec的一个实例处理一种特定类型的数据(例如MP3音频或H.264视频),进行编码或解码操作。
MediaCodec创建: 1.可以使用MediaCodecList为特定的媒体格式创建一个MediaCodec。 可以从MediaExtractor#getTrackFormat获得track的格式。 使用MediaFormat#setFeatureEnabled注入想要添加的任何特性。 然后调用MediaCodecList#findDecoderForFormat来获取能够处理该特定媒体格式的编解码器的名称。 最后,使用createByCodecName(字符串)创建编解码器。
2.还可以使用createDecoder/EncoderByType(java.lang.String)为特定MIME类型创建首选的编解码器。但是,这不能用于注入特性,并且可能会创建一个不能处理特定媒体格式的编解码器。
configure配置codec。
public void configure(
MediaFormat format,
Surface surface, MediaCrypto crypto, int Flags);
MediaFormat format:输入数据的格式(解码器)或输出数据的所需格式(编码器)。传null等同于传递MediaFormat#MediaFormat作为空的MediaFormat。
Surface surface:指定Surface,用于解码器输出的渲染。如果编解码器不生成原始视频输出(例如,不是视频解码器)和/或想配置解码器输出ByteBuffer,则传null。
MediaCrypto crypto:指定一个crypto对象,用于对媒体数据进行安全解密。对于非安全的编解码器,传null。
int flags:当组件是编码器时,flags指定为常量CONFIGURE_FLAG_ENCODE。
MediaFormat:封装描述媒体数据格式的信息(包括音频或视频),以及可选的特性元数据。媒体数据的格式指定为key/value对。key是字符串。值可以integer、long、float、String或ByteBuffer。 特性元数据被指定为string/boolean对。
dequeueInputBufferpublic final int dequeueInputBuffer(long timeoutUs)
返回用于填充有效数据的输入buffer的索引,如果当前没有可用的buffer,则返回-1。 long timeoutUs:等待可用的输入buffer的时间。 如果timeoutUs == 0,则立即返回。 如果timeoutUs < 0,则无限期等待可用的输入buffer。 如果timeoutUs > 0,则等待“timeoutUs”微秒。
【相关学习资料推荐,点击下方链接免费报名,先码住不迷路~】
C 音视频配套学习资料:点击莬费领取→
在指定索引处填充输入buffer后,使用queueInputBuffer将buffer提交给组件。
特定于codec的数据
许多codec要求实际压缩的数据流之前必须有“特定于codec的数据”,即用于初始化codec的设置数据,如 AVC视频中的PPS/SPS。 vorbis音频中的code tables。
public native final void queueInputBuffer(
int index,
int offset, int size, long presentationTimeUs, int flags)
int index:以前调用dequeueInputBuffer(long)返回的输入buffer的索引。 int offset:数据开始时输入buffer中的字节偏移量。 int size:有效输入数据的字节数。 long presentationTimeUs:此buffer的PTS(以微秒为单位)。 int flags:一个由BUFFER_FLAG_CODEC_CONFIG和BUFFER_FLAG_END_OF_STREAM标志组成的位掩码。虽然没有被禁止,但是大多数codec并不对输入buffer使用BUFFER_FLAG_KEY_FRAME标志。
BUFFER_FLAG_END_OF_STREAM:用于指示这是输入数据的最后一部分。
BUFFER_FLAG_CODEC_CONFIG:通过指定这个标志,可以在start()或flush()之后直接提交特定于codec的数据buffer。但是,如果您使用包含这些密钥的媒体格式配置编解码器,它们将在启动后由MediaCodec直接自动提交。因此,不建议使用BUFFER_FLAG_CODEC_CONFIG标志,只建议高级用户使用。
dequeueOutputBuffer从MediaCodec获取输出buffer。
public final int dequeueOutputBuffer(
@NonNull BufferInfo info, long timeoutUs)
返回值:已成功解码的输出buffer的索引或INFO_*常量之一(INFO_TRY_AGAIN_LATER, INFO_OUTPUT_FORMAT_CHANGED 或 INFO_OUTPUT_BUFFERS_CHANGED)。
返回INFO_TRY_AGAIN_LATER而timeoutUs指定为了非负值,表示超时了。 返回INFO_OUTPUT_FORMAT_CHANGED表示输出格式已更改,后续数据将遵循新格式。
BufferInfo info:输出buffer的metadata。 long timeoutUs:含义同dequeueInputBuffer中的timeoutUs参数。
BufferInfo
public final static class BufferInfo {
public void set(
int newOffset, int newSize, long newTimeUs, int newFlags);
public int offset;
public int size;
public long presentationTimeUs;
public int flags;
};
offset:buffer中数据的起始偏移量。 注意设备之间的offset是不一致的。在一些设备上,offset是相对裁剪矩形的左上角像素,而在大多数设备上,offset是相对整个帧的左上角像素。
size:buffer中的数据量(以字节为单位)。如果是0则表示buffer中没有数据,可以丢弃。0大小的buffer的唯一用途是携带流结束标记。
presentationTimeUs:buffer的PTS(以微秒为单位)。来源于相应输入buffer一起传入的PTS。对于大小为0的buffer,应该忽略这个值。
flags:与buffer关联的标识信息,flags包含如下取值: BUFFER_FLAG_KEY_FRAME:buffer包含关键帧的数据。 BUFFER_FLAG_CODEC_CONFIG:buffer包含编解码器初始化/编解码器特定的数据,而不是媒体数据。 BUFFER_FLAG_END_OF_STREAM:标志着流的结束,即在此之后没有buffer可用,除非后面跟着flush。 BUFFER_FLAG_PARTIAL_FRAME:buffer只包含帧的一部分,解码器应该对数据进行批处理,直到在解码帧之前出现没有该标志的buffer为止。
public static final int BUFFER_FLAG_KEY_FRAME = 1;
public static final int BUFFER_FLAG_CODEC_CONFIG = 2;
public static final int BUFFER_FLAG_END_OF_STREAM = 4;
public static final int BUFFER_FLAG_PARTIAL_FRAME = 8;releaseOutputBuffer
使用此方法将输出buffer返回给codec或将其渲染在输出surface。
public void releaseOutputBuffer (int index,
boolean render)
boolean render:如果在配置codec时指定了一个有效的surface,则传递true会将此输出buffer在surface上渲染。一旦不再使用buffer,该surface将把buffer释放回codec。
同步和异步API的使用流程同步API的使用流程- 创建并配置MediaCodec对象。
- 循环直到完成:
- 如果输入buffer准备好了:
- 读取一段输入,将其填充到输入buffer中
- 如果输出buffer准备好了:
- 从输出buffer中获取数据进行处理。
- 处理完毕后,release MediaCodec 对象。
MediaCodec codec = MediaCodec.createByCodecName(name);
codec.configure(format, …);
MediaFormat outputFormat = codec.getOutputFormat(); // option B
codec.start();
for (;;) {
int inputBufferId = codec.dequeueInputBuffer(timeoutUs);
if (inputBufferId >= 0) {
ByteBuffer inputBuffer = codec.getInputBuffer(…);
// fill inputBuffer with valid data
…
codec.queueInputBuffer(inputBufferId, …);
}
int outputBufferId = codec.dequeueOutputBuffer(…);
if (outputBufferId >= 0) {
ByteBuffer outputBuffer = codec.getOutputBuffer(outputBufferId);
MediaFormat bufferFormat = codec.getOutputFormat(outputBufferId); // option A
// bufferFormat is identical to outputFormat
// outputBuffer is ready to be processed or rendered.
…
codec.releaseOutputBuffer(outputBufferId, …);
} else if (outputBufferId == MediaCodec.INFO_OUTPUT_FORMAT_CHANGED) {
// Subsequent data will conform to new format.
// Can ignore if using getOutputFormat(outputBufferId)
outputFormat = codec.getOutputFormat(); // option B
}
}
codec.stop();
codec.release();异步API的使用流程
在Android 5.0, API21,引入了“异步模式”。
- 创建并配置MediaCodec对象。
- 给MediaCodec对象设置回调MediaCodec.Callback
- 在onInputBufferAvailable回调中:
- 读取一段输入,将其填充到输入buffer中
- 在onOutputBufferAvailable回调中:
- 从输出buffer中获取数据进行处理。
- 处理完毕后,release MediaCodec 对象。
C 音视频配套学习资料:点击莬费领取→
MediaCodec codec = MediaCodec.createByCodecName(name);
MediaFormat mOutputFormat; // member variable
codec.setCallback(new MediaCodec.Callback() {
@Override
void onInputBufferAvailable(MediaCodec mc, int inputBufferId) {
ByteBuffer inputBuffer = codec.getInputBuffer(inputBufferId);
// fill inputBuffer with valid data
…
codec.queueInputBuffer(inputBufferId, …);
}
@Override
void onOutputBufferAvailable(MediaCodec mc, int outputBufferId, …) {
ByteBuffer outputBuffer = codec.getOutputBuffer(outputBufferId);
MediaFormat bufferFormat = codec.getOutputFormat(outputBufferId); // option A
// bufferFormat is equivalent to mOutputFormat
// outputBuffer is ready to be processed or rendered.
…
codec.releaseOutputBuffer(outputBufferId, …);
}
@Override
void onOutputFormatChanged(MediaCodec mc, MediaFormat format) {
// Subsequent data will conform to new format.
// Can ignore if using getOutputFormat(outputBufferId)
mOutputFormat = format; // option B
}
@Override
void onError(…) {
…
}
});
codec.configure(format, …);
mOutputFormat = codec.getOutputFormat(); // option B
codec.start();
// wait for processing to complete
codec.stop();
codec.release();
如果你对音视频开发感兴趣,觉得文章对您有帮助,别忘了点赞、收藏哦!或者对本文的一些阐述有自己的看法,有任何问题,欢迎在下方评论区与我讨论!
,