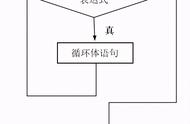
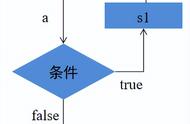
do while语句是一个循环构造,其工作方式与while循环类似,只是该语句总是至少执行一次。执行语句后,do while循环检查条件。如果条件的计算结果为true,则执行路径跳回do-while循环的顶部并再次执行。
实际上,do while循环并不常用。将条件放在循环的底部会模糊循环条件,这可能会导致错误。因此,许多开发人员建议避免do-while循环。
do while的使用频率虽然比while循环和for循环要低,但也有其适用场景,可以让代码更简洁。
1 变量作用域do…while在条件表达式中的作用域需要在do while的大括号{}外(C语言使用{}定义语句块),也就是说,while()中使用的变量不能在do{}内定义,由此,其代码块的封装性比while循环要弱。
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int x = 0; // while()中使用的x 需在do while前声明
do {
printf( "Hello, world!\n" );
} while ( x != 0 );
getchar();
}2 应用场景
2.1 用户交互
#include <stdio.h> /* printf, scanf, puts, NULL */
#include <stdlib.h> /* srand, rand */
#include <time.h> /* time */
int main ()
{
int iSecret, iGuess;
/* initialize random seed: */
srand (time(NULL));
/* generate secret number between 1 and 10: */
iSecret = rand() % 10 1;
do {
printf ("Guess the number (1 to 10): ");
scanf ("%d",&iGuess); // 如果不使用while(),此行代码要写两次
if(iSecret<iGuess) puts ("The secret number is lower");
else if(iSecret>iGuess) puts ("The secret number is higher");
} while(iSecret!=iGuess);
puts ("Congratulations!");
return 0;
}
以下是类似的用户交互情形:
#include <stdio.h>
int main ()
{
int c;
puts ("Enter text. Include a dot ('.') in a sentence to exit:");
do {
c=getchar(); // 如果不使用do while,则此行代码要写在while()内或写两次
putchar (c);
} while(c != '.');
return 0;
}
2.2 读取文件
#include <stdio.h>
int main ()
{
FILE *fp;
int c;
int n = 0;
fp = fopen("file.txt","r");
if(fp == NULL)
{
perror("打开文件时发生错误");
return(-1);
}
do
{
c = fgetc(fp); // 也是一种交互的方式,上面实例也是键盘输入,这里是从磁盘获取数据
if( feof(fp) )
break ;
printf("%c", c);
}while(1);
fclose(fp);
return(0);
}
do while控制结构常用于输入一个字符做判断的情形:
char c;
do{ // do while控制结构常用于输入一个字符做判断的情形
int number;
printf("\ninput number to look for:");
scanf("%d",&number);
//search(number,num,name);
printf("continue ot not(Y/N)?");
fflush(stdin);
scanf("%c",&c );
}while(!(c=='N'||c=='n'));
按条件输入时,do while用起来更自然:
do{
printf("Enter n(1--15):");//要求阶数为1~15 之间的奇数
scanf("%d",&n);
}while( ! ( (n>=1) && ( n <= 15 ) && ( n % 2 != 0 ) ) );
做菜单设计与用户交互时,通常也使用do while。
-End-
,