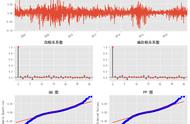
得到数据的概率分布结果
probs = gmm.predict_proba(X)
print(probs[:5].round(3))
[[0. 0.469 0. 0.531]
[1. 0. 0. 0. ]
[1. 0. 0. 0. ]
[0. 0. 0. 1. ]
[1. 0. 0. 0. ]]
编写绘制gmm绘制边界的函数
from matplotlib.patches import Ellipse
def draw_ellipse(position, covariance, ax=None, **kwargs):
"""Draw an ellipse with a given position and covariance"""
ax = ax or plt.gca()
# Convert covariance to principal axes
if covariance.shape == (2, 2):
U, s, Vt = np.linalg.svd(covariance)
angle = np.degrees(np.arctan2(U[1, 0], U[0, 0]))
width, height = 2 * np.sqrt(s)
else:
angle = 0
width, height = 2 * np.sqrt(covariance)
# Draw the Ellipse
for nsig in range(1, 4):
ax.add_patch(Ellipse(position, nsig * width, nsig * height,
angle, **kwargs))
def plot_gmm(gmm, X, label=True, ax=None):
ax = ax or plt.gca()
labels = gmm.fit(X).predict(X)
if label:
ax.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=labels, s=40, cmap=‘viridis‘, zorder=2)
else:
ax.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], s=40, zorder=2)
ax.axis(‘equal‘)
w_factor = 0.2 / gmm.weights_.max()
for pos, covar, w in zip(gmm.means_, gmm.covariances_, gmm.weights_):
draw_ellipse(pos, covar, alpha=w * w_factor)
- 在圆形数据上的聚类结果
gmm = GaussianMixture(n_components=4, random_state=42)
plot_gmm(gmm, X)

- 在偏斜拉伸数据上的聚类结果
gmm = GaussianMixture(n_components=4, covariance_type=‘full‘, random_state=42)
plot_gmm(gmm, X_stretched)

GMM本质上是一个密度估计算法;也就是说,从技术的角度考虑,
一个 GMM 拟合的结果并不是一个聚类模型,而是描述数据分布的生成概率模型。
- 非线性边界的情况
# 构建非线性可分数据
from sklearn.datasets import make_moons
Xmoon, ymoon = make_moons(200, noise=.05, random_state=0)
plt.scatter(Xmoon[:, 0], Xmoon[:, 1]);

? 如果使用2个成分聚类(即废了结果设置为2),基本没什么效果
gmm2 = GaussianMixture(n_components=2, covariance_type=‘full‘, random_state=0)
plot_gmm(gmm2, Xmoon)