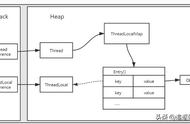
从上述结果可以看出,每个线程只会读取到属于自己的 ThreadLocal 值。
3.ThreadLocal 高级用法① 初始化:initialValuepublic class ThreadLocalByInitExample {
// 定义 ThreadLocal
private static ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal(){
@Override
protected String initialValue() {
System.out.println("执行 initialValue() 方法");
return "默认值";
}
};
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 线程执行任务
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 执行方法,打印线程中数据(未设置值打印)
print(threadName);
}
};
// 创建并启动线程 1
new Thread(runnable, "MyThread-1").start();
// 创建并启动线程 2
new Thread(runnable, "MyThread-2").start();
}
/**
* 打印线程中的 ThreadLocal 值
* @param threadName 线程名称
*/
private static void print(String threadName) {
// 得到 ThreadLocal 中的值
String result = threadLocal.get();
// 打印结果
System.out.println(threadName " 得到值:" result);
}
}
以上程序的执行结果为:

当使用了 #threadLocal.set 方法之后,initialValue 方法就不会被执行了,如下代码所示:
public class ThreadLocalByInitExample {
// 定义 ThreadLocal
private static ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal() {
@Override
protected String initialValue() {
System.out.println("执行 initialValue() 方法");
return "默认值";
}
};
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 线程执行任务
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println(threadName " 存入值:" threadName);
// 在 ThreadLocal 中设置值
threadLocal.set(threadName);
// 执行方法,打印线程中设置的值
print(threadName);
}
};
// 创建并启动线程 1
new Thread(runnable, "MyThread-1").start();
// 创建并启动线程 2
new Thread(runnable, "MyThread-2").start();
}
/**
* 打印线程中的 ThreadLocal 值
* @param threadName 线程名称
*/
private static void print(String threadName) {
try {
// 得到 ThreadLocal 中的值
String result = threadLocal.get();
// 打印结果
System.out.println(threadName "取出值:" result);
} finally {
// 移除 ThreadLocal 中的值(防止内存溢出)
threadLocal.remove();
}
}
}
以上程序的执行结果为:

要理解这个问题,需要从 ThreadLocal.get() 方法的源码中得到答案,因为初始化方法 initialValue 在 ThreadLocal 创建时并不会立即执行,而是在调用了 get 方法只会才会执行,测试代码如下:
import java.util.Date;
public class ThreadLocalByInitExample {
// 定义 ThreadLocal
private static ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal() {
@Override
protected String initialValue() {
System.out.println("执行 initialValue() 方法 " new Date());
return "默认值";
}
};
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 线程执行任务
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 得到当前线程名称
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
// 执行方法,打印线程中设置的值
print(threadName);
}
};
// 创建并启动线程 1
new Thread(runnable, "MyThread-1").start();
// 创建并启动线程 2
new Thread(runnable, "MyThread-2").start();
}
/**
* 打印线程中的 ThreadLocal 值
* @param threadName 线程名称
*/
private static void print(String threadName) {
System.out.println("进入 print() 方法 " new Date());
try {
// 休眠 1s
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 得到 ThreadLocal 中的值
String result = threadLocal.get();
// 打印结果
System.out.println(String.format("%s 取得值:%s %s",
threadName, result, new Date()));
}
}
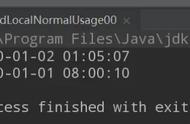
以上程序的执行结果为:

从上述打印的时间可以看出:initialValue 方法并不是在 ThreadLocal 创建时执行的,而是在调用 Thread.get 方法时才执行的。
接下来来看 Threadlocal.get 源码的实现:
public T get() {
// 得到当前的线程
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
// 判断 ThreadLocal 中是否有数据
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
// 有 set 值,直接返回数据
return result;
}
}
// 执行初始化方法【重点关注】
return setInitialValue();
}
private T setInitialValue() {
// 执行初始化方法【重点关注】
T value = initialValue();
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
return value;
}
从上述源码可以看出,当 ThreadLocal 中有值时会直接返回值 e.value,只有 Threadlocal 中没有任何值时才会执行初始化方法 initialValue。
注意事项—类型必须保持一致注意在使用 initialValue 时,返回值的类型要和 ThreadLoca 定义的数据类型保持一致,如下图所示: