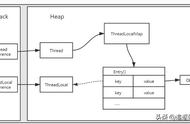
如果数据不一致就会造成 ClassCaseException 类型转换异常,如下图所示:

import java.util.function.Supplier;
public class ThreadLocalByInitExample {
// 定义 ThreadLocal
private static ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal =
ThreadLocal.withInitial(new Supplier<String>() {
@Override
public String get() {
System.out.println("执行 withInitial() 方法");
return "默认值";
}
});
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 线程执行任务
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
// 执行方法,打印线程中设置的值
print(threadName);
}
};
// 创建并启动线程 1
new Thread(runnable, "MyThread-1").start();
// 创建并启动线程 2
new Thread(runnable, "MyThread-2").start();
}
/**
* 打印线程中的 ThreadLocal 值
* @param threadName 线程名称
*/
private static void print(String threadName) {
// 得到 ThreadLocal 中的值
String result = threadLocal.get();
// 打印结果
System.out.println(threadName " 得到值:" result);
}
}
以上程序的执行结果为:

通过上述的代码发现,withInitial 方法的使用好和 initialValue 好像没啥区别,那为啥还要造出两个类似的方法呢?客官莫着急,继续往下看。
③ 更简洁的 withInitial 使用withInitial 方法的优势在于可以更简单的实现变量初始化,如下代码所示:
public class ThreadLocalByInitExample {
// 定义 ThreadLocal
private static ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> "默认值");
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 线程执行任务
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
// 执行方法,打印线程中设置的值
print(threadName);
}
};
// 创建并启动线程 1
new Thread(runnable, "MyThread-1").start();
// 创建并启动线程 2
new Thread(runnable, "MyThread-2").start();
}
/**
* 打印线程中的 ThreadLocal 值
* @param threadName 线程名称
*/
private static void print(String threadName) {
// 得到 ThreadLocal 中的值
String result = threadLocal.get();
// 打印结果
System.out.println(threadName " 得到值:" result);
}
}
以上程序的执行结果为:

了解了 ThreadLocal 的使用之后,我们回到本文的主题,接下来我们将使用 ThreadLocal 来实现 1000 个时间的格式化,具体实现代码如下:
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class MyThreadLocalByDateFormat {
// 创建 ThreadLocal 并设置默认值
private static ThreadLocal<SimpleDateFormat> dateFormatThreadLocal =
ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> new SimpleDateFormat("mm:ss"));
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建线程池执行任务
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(10, 10, 60,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(1000));
// 执行任务
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i ) {
int finalI = i;
// 执行任务
threadPool.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 得到时间对象
Date date = new Date(finalI * 1000);
// 执行时间格式化
formatAndPrint(date);
}
});
}
// 线程池执行完任务之后关闭
threadPool.shutdown();
// 线程池执行完任务之后关闭
threadPool.shutdown();
}
/**
* 格式化并打印时间
* @param date 时间对象
*/
private static void formatAndPrint(Date date) {
// 执行格式化
String result = dateFormatThreadLocal.get().format(date);
// 打印最终结果
System.out.println("时间:" result);
}
}
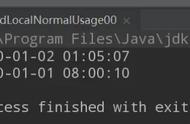
以上程序的执行结果为: