01. 前言
面向对象编程(OOP)并不是一种特定的语言或者工具,它只是一种设计方法、设计思想。它表现出来的三个最基本的特性就是封装、继承与多态。很多面向对象的编程语言已经包含这三个特性了,例如Smalltalk、C 、Java。但是你也可以用几乎所有的编程语言来实现面向对象编程,例如 ANSI-C。要记住,面向对象是一种思想,一种方法,不要太拘泥于编程语言。
C语言不是面向对象的语言,因此使用C语言完全实现面向对象的编程是不可能。但是使用C语言可以很容易实现基于对象的编程,并且基本实现对象的封装性,部分实现对象的继承。
02. 简单程序示例
C语言实现对象封装的小程序,包含三部分:接口,调用和实现,均使用C语言的基本语法实现。
头文件test.h声明如下
#ifndef __TEST_H__
#define __TEST_H__
#ifdef __cplusplus
//表示是C语言的头文件
extern "C"
{
#endif
typedef void * HPERSON;
//创建对象
HPERSON createPerson(const char *name);
//设置对象
void setPerson(HPERSON person, int age, int id);
//显示对象
void displayPerson(HPERSON person);
//删除对象
void deletePerson(HPERSON person);
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif /*__TEST_H__*/
test.c文件如下
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "test.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define NAMEMAX 32
//Person表示HPERSON句柄指向的结构体
typedef struct _Person {
char name[NAMEMAX];
int age;
int id;
}Person;
//创建对象
HPERSON createPerson(const char * name)
{
Person *p = NULL;
printf("创建对象\n");
if (strlen(name) 1 <= NAMEMAX)
{
p = malloc(sizeof(Person));
if (NULL == p)
{
printf("分配内存失败\n");
return NULL;
}
memset(p, 0, sizeof(Person));
strcpy(p->name, name);
p->age = 0;
p->id = 0;
}
return p;
}
//设置对象
void setPerson(HPERSON person, int age, int id)
{
Person *p = person;
if (NULL != p)
{
p->age = age;
p->id = id;
}
}
//显示对象
void displayPerson(HPERSON person)
{
Person *p = person;
if (NULL == p)
{
printf("displayPerson 参数非法\n");
return;
}
printf("Name: %s age: %d id:%d\n", p->name, p->age, p->id);
}
//删除对象
void deletePerson(HPERSON person)
{
free(person);
}
main.c实现如下
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include "test.h"
int main()
{
HPERSON p = createPerson("LiMing");
setPerson(p, 18, 1);
displayPerson(p);
deletePerson(p);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
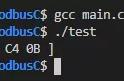
测试结果
创建对象
Name: LiMing age: 18 id:1
请按任意键继续. . .
总结
对象的操作一直使用句柄HPERSON,在调用的过程中看不到程序处理的细节,比如对象的建立和释放。接口掩盖了实现的很多细节,在接口中看不到指针的使用,并且不能够也没有必要访问数据结构。
03. 程序示例优化
头文件test.h声明如下
#ifndef __TEST_H__
#define __TEST_H__
#ifdef __cplusplus
//表示是C语言的头文件
extern "C"
{
#endif
typedef void * HPERSON;
//创建对象
HPERSON createPerson(const char *name);
//设置对象
void setPerson(HPERSON person, int age, int id);
//显示对象
void displayPerson(HPERSON person);
//删除对象
void deletePerson(HPERSON person);
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif /*__TEST_H__*/
test.c文件实现如下
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "test.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
//Person表示HPERSON句柄指向的结构体
typedef struct _Person
{
//使用指针
char *name;
int age;
int id;
}Person;
//创建对象
HPERSON createPerson(const char * name)
{
Person *p = NULL;
printf("创建对象\n");
p = malloc(sizeof(Person));
if (NULL == p)
{
printf("分配内存失败\n");
return NULL;
}
memset(p, 0, sizeof(Person));
p->name = malloc(strlen(name) 1);
if (NULL == p->name)
{
printf("分配内存失败\n");
return NULL;
}
strcpy(p->name, name);
p->age = 0;
p->id = 0;
return p;
}
//设置对象
void setPerson(HPERSON person, int age, int id)
{
Person *p = person;
if (NULL != p)
{
p->age = age;
p->id = id;
}
}
//显示对象
void displayPerson(HPERSON person)
{
Person *p = person;
if (NULL == p)
{
printf("displayPerson 参数非法\n");
return;
}
printf("Name: %s age: %d id:%d\n", p->name, p->age, p->id);
}
//删除对象
void deletePerson(HPERSON person)
{
Person *p = person;
if (NULL == person)
{
return;
}
if (NULL != p->name)
{
free(p->name);
}
free(person);
}
main.c测试代码
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include "test.h"
int main()
{
HPERSON p = createPerson("LiMing");
setPerson(p, 18, 1);
displayPerson(p);
deletePerson(p);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
测试结果
创建对象
Name: LiMing age: 18 id:1
请按任意键继续. . .
04. 总结
基于对象的C语言编程的流程,程序从接口到实现都是使用C语言实现的。
,