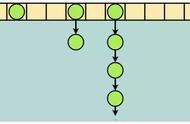
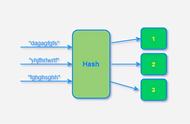
- HashMap01 的实现只是通过哈希计算出的下标,散列存放到固定的数组内。那么这样当发生元素下标碰撞时,原有的元素就会被新的元素替换掉。
测试
@Test
public void test_hashMap01() {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap01<>();
map.put("01", "花花");
map.put("02", "豆豆");
logger.info("碰撞前 key:{} value:{}", "01", map.get("01"));
// 下标碰撞
map.put("09", "蛋蛋");
map.put("12", "苗苗");
logger.info("碰撞前 key:{} value:{}", "01", map.get("01"));
}

06:58:41.691 [main] INFO cn.bugstack.algorithms.test.AlgorithmsTest - 碰撞前 key:01 value:花花
06:58:41.696 [main] INFO cn.bugstack.algorithms.test.AlgorithmsTest - 碰撞前 key:01 value:苗苗
Process finished with exit code 0
- 通过测试结果可以看到,碰撞前 map.get("01") 的值是花花,两次下标索引碰撞后存放的值则是苗苗
- 这也就是使用哈希散列必须解决的一个问题,无论是在已知元素数量的情况下,通过扩容数组长度解决,还是把碰撞的元素通过链表存放,都是可以的。
说明:既然我们没法控制元素不碰撞,但我们可以对碰撞后的元素进行管理。比如像 HashMap 中拉链法一样,把碰撞的元素存放到链表上。这里我们就来简化实现一下。
public class HashMap02BySeparateChaining<K, V> implements Map<K, V> {
private final LinkedList<Node<K, V>>[] tab = new LinkedList[8];
@Override
public void put(K key, V value) {
int idx = key.hashCode() & (tab.length - 1);
if (tab[idx] == null) {
tab[idx] = new LinkedList<>();
tab[idx].add(new Node<>(key, value));
} else {
tab[idx].add(new Node<>(key, value));
}
}
@Override
public V get(K key) {
int idx = key.hashCode() & (tab.length - 1);
for (Node<K, V> kvNode : tab[idx]) {
if (key.equals(kvNode.getKey())) {
return kvNode.value;
}
}
return null;
}
static class Node<K, V> {
final K key;
V value;
public Node(K key, V value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
public K getKey() {
return key;
}
public V getValue() {
return value;
}
}
}

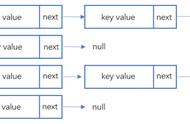
- 因为元素在存放到哈希桶上时,可能发生下标索引膨胀,所以这里我们把每一个元素都设定成一个 Node 节点,这些节点通过 LinkedList 链表关联,当然你也可以通过 Node 节点构建出链表 next 元素即可。
- 那么这时候在发生元素碰撞,相同位置的元素就都被存放到链表上了,获取的时候需要对存放多个元素的链表进行遍历获取。
测试
@Test
public void test_hashMap02() {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap02BySeparateChaining<>();
map.put("01", "花花");
map.put("05", "豆豆");
logger.info("碰撞前 key:{} value:{}", "01", map.get("01"));
// 下标碰撞
map.put("09", "蛋蛋");
map.put("12", "苗苗");
logger.info("碰撞前 key:{} value:{}", "01", map.get("01"));
}

07:21:16.654 [main] INFO cn.bugstack.algorithms.test.AlgorithmsTest - 碰撞前 key:01 value:花花
07:22:44.651 [main] INFO cn.bugstack.algorithms.test.AlgorithmsTest - 碰撞前 key:01 value:花花
Process finished with exit code 0
- 此时第一次和第二次获取01位置的元素就都是花花了,元素没有被替代。因为此时的元素是被存放到链表上了。
说明:除了对哈希桶上碰撞的索引元素进行拉链存放,还有不引入新的额外的数据结构,只是在哈希桶上存放碰撞元素的方式。它叫开放寻址,也就是 ThreaLocal 中运用斐波那契散列 开放寻址的处理方式。
public class HashMap03ByOpenAddressing<K, V> implements Map<K, V> {
private final Node<K, V>[] tab = new Node[8];
@Override
public void put(K key, V value) {
int idx = key.hashCode() & (tab.length - 1);
if (tab[idx] == null) {
tab[idx] = new Node<>(key, value);
} else {
for (int i = idx; i < tab.length; i ) {
if (tab[i] == null) {
tab[i] = new Node<>(key, value);
break;
}
}
}
}
@Override
public V get(K key) {
int idx = key.hashCode() & (tab.length - 1);
for (int i = idx; i < tab.length; i ){
if (tab[idx] != null && tab[idx].key == key) {
return tab[idx].value;
}
}
return null;
}
static class Node<K, V> {
final K key;
V value;
public Node(K key, V value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
}