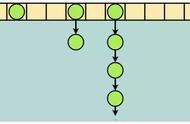
- 开放寻址的设计会对碰撞的元素,寻找哈希桶上新的位置,这个位置从当前碰撞位置开始向后寻找,直到找到空的位置存放。
- 在 ThreadLocal 的实现中会使用斐波那契散列、索引计算累加、启发式清理、探测式清理等操作,以保证尽可能少的碰撞。
测试
@Test
public void test_hashMap03() {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap03ByOpenAddressing<>();
map.put("01", "花花");
map.put("05", "豆豆");
logger.info("碰撞前 key:{} value:{}", "01", map.get("01"));
// 下标碰撞
map.put("09", "蛋蛋");
map.put("12", "苗苗");
logger.info("碰撞前 key:{} value:{}", "01", map.get("01"));
}

07:20:22.382 [main] INFO cn.bugstack.algorithms.test.AlgorithmsTest - 碰撞前 key:01 value:花花
07:20:22.387 [main] INFO cn.bugstack.algorithms.test.AlgorithmsTest - 碰撞前 key:01 value:花花
07:20:22.387 [main] INFO cn.bugstack.algorithms.test.AlgorithmsTest - 数据结构:HashMap{tab=[null,{"key":"01","value":"花花"},{"key":"09","value":"蛋蛋"},{"key":"12","value":"苗苗"},null,{"key":"05","value":"豆豆"},null,null]}
Process finished with exit code 0
- 通过测试结果可以看到,开放寻址对碰撞元素的寻址存放,也是可用解决哈希索引冲突问题的。
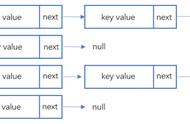
说明:合并散列是开放寻址和单独链接的混合,碰撞的节点在哈希表中链接。此算法适合固定分配内存的哈希桶,通过存放元素时识别哈希桶上的最大空槽位来解决合并哈希中的冲突。
public class HashMap04ByCoalescedHashing<K, V> implements Map<K, V> {
private final Node<K, V>[] tab = new Node[8];
@Override
public void put(K key, V value) {
int idx = key.hashCode() & (tab.length - 1);
if (tab[idx] == null) {
tab[idx] = new Node<>(key, value);
return;
}
int cursor = tab.length - 1;
while (tab[cursor] != null && tab[cursor].key != key) {
--cursor;
}
tab[cursor] = new Node<>(key, value);
// 将碰撞节点指向这个新节点
while (tab[idx].idxOfNext != 0){
idx = tab[idx].idxOfNext;
}
tab[idx].idxOfNext = cursor;
}
@Override
public V get(K key) {
int idx = key.hashCode() & (tab.length - 1);
while (tab[idx].key != key) {
idx = tab[idx].idxOfNext;
}
return tab[idx].value;
}
static class Node<K, V> {
final K key;
V value;
int idxOfNext;
public Node(K key, V value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
}

- 合并散列的最大目的在于将碰撞元素链接起来,避免因为需要寻找碰撞元素所发生的循环遍历。也就是A、B元素存放时发生碰撞,那么在找到A元素的时候可以很快的索引到B元素所在的位置。
测试
07:18:43.613 [main] INFO cn.bugstack.algorithms.test.AlgorithmsTest - 碰撞前 key:01 value:花花
07:18:43.618 [main] INFO cn.bugstack.algorithms.test.AlgorithmsTest - 碰撞前 key:01 value:苗苗
07:18:43.619 [main] INFO cn.bugstack.algorithms.test.AlgorithmsTest - 数据结构:HashMap{tab=[null,{"idxOfNext":7,"key":"01","value":"花花"},null,null,null,{"idxOfNext":0,"key":"05","value":"豆豆"},{"idxOfNext":0,"key":"12","value":"苗苗"},{"idxOfNext":6,"key":"09","value":"蛋蛋"}]}
Process finished with exit code 0
- 相对于直接使用开放寻址,这样的挂在链路指向的方式,可以提升索引的性能。因为在实际的数据存储上,元素的下一个位置不一定空元素,可能已经被其他元素占据,这样就增加了索引的次数。所以使用直接指向地址的方式,会更好的提高索引性能。
说明:这个名字起的比较有意思,也代表着它的数据结构。杜鹃鸟在孵化的时候,雏鸟会将其他蛋或幼崽推出巢穴;类似的这个数据结构会使用2组key哈希表,将冲突元素推到另外一个key哈希表中。
private V put(K key, V value, boolean isRehash) {
Object k = maskNull(key);
if (containsKey(k)) {
return null;
}
if (insertEntry(new Entry<K, V>((K) k, value))) {
if (!isRehash) {
size ;
}
return null;
}
rehash(2 * table.length);
return put((K) k, value);
}
private boolean insertEntry(Entry<K, V> e) {
int count = 0;
Entry<K, V> current = e;
int index = hash(hash1, current.key);
while (current != e || count < table.length) {
Entry<K, V> temp = table[index];
if (temp == null) {
table[index] = current;
return true;
}
table[index] = current;
current = temp;
if (index == hash(hash1, current.key)) {
index = hash(hash2, current.key);
} else {
index = hash(hash1, current.key);
}
count;
}
return false;
}

- 当多个键映射到同一个单元格时会发生这种情况。杜鹃散列的基本思想是通过使用两个散列函数而不是仅一个散列函数来解决冲突。
- 这为每个键在哈希表中提供了两个可能的位置。在该算法的一种常用变体中,哈希表被分成两个大小相等的较小的表,每个哈希函数都为这两个表之一提供索引。两个散列函数也可以为单个表提供索引。
- 在实践中,杜鹃哈希比线性探测慢约 20-30%,线性探测是常用方法中最快的。然而,由于它对搜索时间的最坏情况保证,当需要实时响应率时,杜鹃散列仍然很有价值。杜鹃散列的一个优点是它的无链接列表属性,非常适合 GPU 处理。
测试