1. 宾语从句
宾语从句是指在一个句子中充当宾语的句子
如:I'm extremely sorry that I have lost your book.
宾语从句注意事项:
①宾语从句的连接词
②宾语从句用陈述语序
③宾语从句的时态
(1)宾语从句的连接词:宾语从句的连接词包括that、if/whether(是否)、特殊疑问词。(详情见上次宾语从句单讲)
(2)宾语从句的语序:
A. 宾语从句的连接词后加陈述语序(主语在前,谓语在后)
例如:I'm wondering if they would believe in me.
B. 当连接词本身又是宾语从句的主语时,后面直接加谓语动词
如:He asked me who had helped him.
(3)宾语从句的时态,只要记住以下口诀就可以了“主现从任,主过从过,客观真理一般现”
A. 主现从任:主句如果是一般现在时,则从句根据时间状语需要从八种时态中任选一种,根据句意
如:1.He tells me he likes maths very much(一般现在时)
I know he didn't tell you that he would come then.(过去时态)
B. 主过从过:主句如果是一般过去时,则从句根据时间状语需要从四种带“过”字的时态中任选一种,带“过”字的时态分别是如:一般过去时,过去进行时,过去将来时,过去完成时。
如:She told me that she liked playing basketball(一般过去时)
C. 客观真理一般现:客观真理永远用一般现在时。
如:1.My teacher says the moon goes around the earth.
★ 做题时,往往会遇到宾语从句否定转移的情况,当主句谓语表示“想,认为”等意义的动词,如:think.believe.imagine.suppose.expect.guess等,从句的否定一般要转移到主句,其反义疑问句一般与宾语保持一致,且用肯定形式。
例如:I don't think they will wait to the last minute.
I didn't believe that was his fault,was it?
2. 状语从句
(1)时间状语从句:在一个句子中作时间状语的句子。
时间状语的连接词:when(当…时候) while(当…时候) as(当…时候) after(在…以后) before(在…以前) as soon as(一…就) since(自从…到现在) till /until(直到…才) by the time(到…为止)
连接词后加陈述语序。
例:It was snowing when we got to the airport.
(2)原因状语从句:在一个句子中作原因状语的句子。
连接词:由连词because, since, as等词引导。
★ because 意为“因为”,表示造成某种情况的直接原因,语气最强,常用“why”提问
举例:He took off his coat because it was too hot in the room.
★ since往往表示众所周知的原因,多意为“既然” since从句通常位于主句之前,其语气比as稍强。
例如:Since you won't help me,I'll ask someone else.
★ as表示原因时,语气最弱,意为“由于”
例如:As you were out,I left a message for you.
(3)条件状语从句:在一个句子中作条件状语的句子。
连接词:if如果, unless (=if not) 除非,as/so long as(只要),once(一旦)
举例:If I am free tomorrow,I will help you with your English.
(4)目的、结果状语从句
目的状语从句连接词so that, in order that 引导。
例如:Speak louder so that the people in the hall can all hear you.
结果状语从句连接词 so…that, such…that, so( that)
举例:so…that 如此…以至于
I'm so knowledgeable that I can help students study.
★ so that 引导目的状语和结果状语的区分:
1.意思有区别
表示目的状语从句时,意思为: 以便, 为了,为使。
表示结果状语从句时,意思为: 结果是,所以。
2.引导目的状语从句常常与can, could,may,might,will,would,shall,should,等连用.
例如:So that everyone will notice her,she dresses like an angel.
3.引导目的状语从句通常不用逗号隔开,引导结果状语从句一般有逗号隔开。
例如:We’ll come at eight so that the meeting can begin early.(目的状语)
We arrived early in the morning,so that we caught the first train.(结果状语)
(5)让步状语从句
让步状语从句是指在句子中作让步的状语的句子
连接词: though, although,even though,even if
though/although引导让步状语从句时,主句中不能再用but,但可以用yet
举例:Although he is rich, yet he is not happy.
no matter引导让步状语从句:
结构:"no matter 特殊疑问词疑问词 陈述语序" 或"特殊疑问词 后缀ever 陈述语序"
如:whenever I'm unhappy, it is my friend who cheers me up.=No matter when I'm unhappy, it is my friend who cheers me up.
类似此类还有:
whatever=no matter what
wherever=no matter where
whoever=no matter who
however=no matter how
whenever=no matter when
注意:no matter 不能引导主语从句和宾语从句。
(6)地点状语从句
在句中作地点状语的从句称为地点状语从句,可至于句首句中和句尾。常见引导词有where,wherever等。
例句:We live where the road crosses the river.
(7)方式状语从句
方式状语从句常见引导词有:as(如同,按...方式),as if,as though等
★ 方式状语从句所表示的情况是事实或可能性很大时,通常用陈述语气。
例如:She looked a bit strange,as if/as though she knew something.
★ 方式状语从句所表示的情况不是事实,通常用虚拟语气,表示现在的情况用过去时,表示过去的情况用过去完成时。
例如:I remember the whole thing as if/as though it happened yesterday.
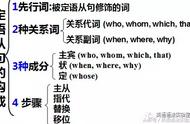
3. 定语从句
定语是指在句子中用来修饰名词、代词的成分。
如:I will give my mother a bunch of beautiful flower.(中beautiful就是定语)
定语从句是指在一个句子中作定语的句子,定语从句要放在所修饰的词后
如:I have met the doctor who is in the No.1 hospital.
定语从句的连接词:
连接代词:who、which、whom、whose、that
连接副词:when、where、why
关系代词介绍:
who:指人,在从句中可充当主语,宾语
whom:指人,在从句中充当宾语
that:指人/物,在从句中充当主语,宾语,表语
which:指物,在从句中充当主语,宾语
whose:指人/物,在从句中充当定语
This is an old computer. It works much slower.→
This is an old computer which/that works much slower.
关系副词介绍:
when:在从句中充当时间状语,先行词一般为day,year,date,time等表示时间的名词
where:在从句中充当地点状语,先行词一般为place,city,Beijing等表示地点的名词
why:在从句中充当原因状语,先行词为表示原因的名词,如reason
关于定语从句的详细讲解请关注下次分享
,