案例一、累加和累乘(for循环)今天小会来给大家分享几个循环案例,从例子中体验编程的乐趣,话不多说,一起来看看吧。
需求:
1、计算0-100的累加和。
2、计算0-100的偶数的累加和。
3、计算0-100的奇数的累加和。
4、计算a-b的累加和。
5、输入一个数字计算这个数字的阶乘。
代码:
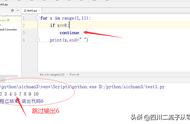
#累加问题1:0-100的累加和
s = 0for i in range(0,101):#可以等价写为:#for i in range(100,0,-1):
s = iprint(s)
#累加问题2:0-100的偶数和
s = 0for i in range(0,101,2):
s = i;print(s)
#累加问题3:0-100的奇数和
s = 0for i in range(1,101,2):
s = iprint(s)
#计算a-b的累加和
a,b = eval(input("请输入a和b的值:"))
s = 0for i in range(a, b 1):
s = iprint(s)
#计算阶乘#如4! = 4*3*2*1 = 1*2*3*4
a = eval(input("请输入一个数字计算其阶乘:"))
s = 1for i in range(1,a 1):
s *= iprint(s)案例二、实现死循环
需求:
1、使用while循环,实现死循环。
2、使用for循环,实现死循环。
代码:
while循环:
while True:
...
...
语句
...
...
for循环:
#使用for来实现死循环class Infinite: #定义一个可以无限迭代的类
def __iter__(self):
return self
def __next__(self):
return None #每次迭代本类对象的时候,返回None
#死循环
i = 0for obj in Infinite():
print(i)
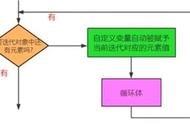
i =1案例三、计算人数(continue语句的使用)
需求:
循环输入5个玩家的消费,统计消费额低于500的玩家数量。如果消费大于等于500,则跳过,小于500则计数器 1。
代码:
#计算人数(continue语句的使用)
#循环输入5个玩家的消费,统计消费额低于500的玩家数量#如果消费大于等于500,则跳过,小于500则计数器 1
ans = 0 #计数器
money = 0 #玩家消费额
for i in range(5):
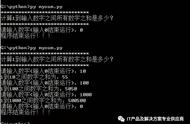
money = eval(input("请输入第{}个玩家的消费金额:".format(i 1)))
if money>=500:
continue
ans = 1
#另一种写法:
#if money < 500:
# ans = 1print("消费金额大于等于500的玩家有{}个,小于500的玩家有{}个".format(5-ans,ans))案例四、打印十行十列★,隔行换色
需求:
打印十行十列★,隔行换色
代码:
# 方法一:while循环
i = 1
while i <= 10:
j = 1
while j <= 10:
if j % 2 == 1:
print("★",end="")
else:
print("☆",end="")
j = 1
i = 1
print()
# 方法二:for循环
for i in range(1,11):
for j in range(1,11):
if j % 2 == 1:
print("★",end="")
else:
print("☆",end="")
print()
案例五、百钱买百鸡
需求:
公鸡 母鸡 小鸡
公鸡1块钱1只,母鸡3块钱一只,小鸡5毛钱一只
问: 用100块钱买100只鸡,有多少种买法?
代码:
# 方法一:while循环
count = 0
x = 0
while x <= 100:
y = 0
while y <= 33:
z = 0
while z <= 100:
if x y z == 100 and x 3*y 0.5*z == 100:
count = 1
z = 1
y = 1
x = 1
print(count)
# 方法二:for循环
count = 0
for x in range(0,101):
for y in range(0,34):
for z in range(0,101):
if x y z == 100 and x 3*y 0.5*z == 100:
count = 1
print(count)
今天的案例分享就到这里了,鼓励大家多尝试一下哦!如果有兴趣学习Python的小伙伴,可以看看这门《嘿有趣之Python快速入门》课程,免费学习哦!点击【了解更多】查看课程哦
,