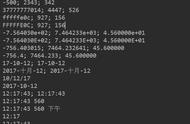
如题:假设有A、B 2个线程,分别依次输出1a2b3c4d,A线程输出数字,B线程输出字母。
下面有几种方法,感觉方法1是最容易想到的。
方法1:synchronized 和 wait/notify
/**
* 使用 synchronized 和 wait notify
*/
private static void func1() {
char[] num = new char[]{'1', '2', '3', '4'};
char[] str = new char[]{'A', 'B', 'C', 'D'};
Object lock = new Object();
AtomicBoolean printChar = new AtomicBoolean(true);
new Thread("T1") {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock) {
for (char c : num) {
try {
while (printChar.get()) {
printChar.set(false);
System.out.println(getName() " >>> " c);
lock.notify();
}
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
lock.notify(); // 这行一定要加,不然会在所有数据遍历完成后T2线程还是wait状态
}
}
}.start();
// 防止有的虚拟机上不是先输出数字的
try {
Thread.sleep(20);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread("T2") {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock) {
for (char c : str) {
try {
while (!printChar.get()) {
printChar.set(true);
System.out.println(getName() " >>> " c);
lock.notify();
}
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 这一行是可以去掉的,因为T2线程遍历完最后一个数据会通过notify唤醒T1线程
// lock.notify();
}
}
}.start();
}
方法2:ReentrantLock 加 Condition
/**
* 使用 ReentrantLock 加 Condition
*/
private static void func2() {
char[] num = new char[]{'1', '2', '3', '4'};
char[] str = new char[]{'A', 'B', 'C', 'D'};
ReentrantLock reentrantLock = new ReentrantLock(true);
Condition printCharCondition = reentrantLock.newCondition();
Condition printNumCondition = reentrantLock.newCondition();
new Thread("T1") {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
reentrantLock.lock();
for (char c : num) {
System.out.println(getName() " >>> " c);
printCharCondition.signal();
printNumCondition.await();
}
printCharCondition.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
reentrantLock.unlock();
}
}
}.start();
new Thread("T2") {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
reentrantLock.lock();
for (char c : str) {
System.out.println(getName() " >>> " c);
printNumCondition.signal();
printCharCondition.await();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
reentrantLock.unlock();
}
}
}.start();
}
方法3:使用信号量 Semaphore
/**
* 使用 Semaphore
*/
private static void func3() {
char[] num = new char[]{'1', '2', '3', '4'};
char[] str = new char[]{'A', 'B', 'C', 'D'};
Semaphore printNum = new Semaphore(1);
Semaphore printChar = new Semaphore(0);
new Thread("T1") {
@Override
public void run() {
for (char c : num) {
try {
printNum.acquire();
System.out.println(getName() " >>> " c);
printChar.release();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}.start();
new Thread("T2") {
@Override
public void run() {
for (char c : str) {
try {
printChar.acquire();
System.out.println(getName() " >>> " c);
printNum.release();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}.start();
}
方法4:使用自旋
/**
* 使用自旋
*/
private static void func4() {
char[] num = new char[]{'1', '2', '3', '4'};
char[] str = new char[]{'A', 'B', 'C', 'D'};
AtomicBoolean printNum = new AtomicBoolean(true);
new Thread("T1") {
@Override
public void run() {
for (char c : num) {
while (!printNum.get()) {}
System.out.println(getName() " >>> " c);
printNum.set(false);
/**
* 注意,上面的while循环的判断一定要加 !,否则后续的都可能无法输出了,如下写法就可能后续的无法输出
*/
// while (printNum.get()) {
// System.out.println(getName() " >>> " c);
// printNum.set(false);
// }
}
}
}.start();
new Thread(("T2")) {
@Override
public void run() {
for (char c : str) {
while (printNum.get()) {}
System.out.println(getName() " >>> " c);
printNum.set(true);
// while (!printNum.get()) {
// System.out.println(getName() " >>> " c);
// printNum.set(true);
// }
}
}
}.start();
}
,