136 化学元素的质量数
Mass Number of Chemical Elements
(https://www.nuclear-power.com/)
化学元素的质量数
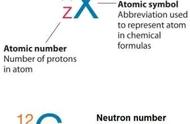
The total number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the neutron number of the atom and is given the symbol N. Neutron number plus atomic number equals atomic mass number: N Z=A. The difference between the neutron number and the atomic number is known as the neutron excess: D = N – Z = A – 2Z.
原子核内的中子总数称为该原子的中子数,用符号N表示。中子数 原子序数等于原子质量数:N Z=A。中子数和原子序数之间的差异被称为中子过剩:D = N - Z = A - 2Z。
Neutron number is rarely written explicitly in nuclide symbol notation, but appears as a subscript to the right of the element symbol. Nuclides that have the same neutron number but a different proton number are called isotones. The various species of atoms whose nuclei contain particular numbers of protons and neutrons are called nuclides. Each nuclide is denoted by chemical symbol of the element (this specifies Z) with tha atomic mass number as supescript. Therefore, we cannot determine the neutron number of uranium, for example. We can determine the neutron number of certain isotope. For example, the neutron number of uranium-238 is 238-92=146.
在核素符号标记时很少会直接写出中子数,但可以元素符号右侧的下标形式出现。具有相同中子数但不同质子数的核素称为同中子异荷素。原子核中含有特定数量的质子和中子的各种原子称为核素。每个核素用该元素的化学符号表示(这指定了Z),以原子质量数为上标。因此,举例说明,我们不能确定铀的中子数。我们可以确定某些同位素的中子数。例如,铀238的中子数为238-92=146。
注:
(以下内容来自百度百科)

质量数(Mass number)是指中性原子中,将原子内所有质子和中子的相对质量取近似整数值相加而得到的数值。由于一个质子和一个中子相对质量取近似整数值时均为1,所以质量数(A)=质子数(Z) 中子数(N)。
(待续)
,