138 中子数
Neutron Number
(https://www.nuclear-power.com/)
中子数
The neutron number is the total number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is given the symbol N. Neutron number plus atomic number equals atomic mass number: N Z=A.
中子数是原子核内中子的总数,符号为N。中子数加原子序数等于原子质量数:N Z=A。
The atom consists of a small but massive nucleus surrounded by a cloud of rapidly moving electrons. The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons, and the total number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the neutron number of the atom and is given the symbol N.
原子由一个小而致密的原子核组成,原子核周围环绕着一团快速移动的电子。原子核由质子和中子组成,原子核内的中子总数称为该原子的中子数,用符号N表示。

Neutron number plus atomic number equal atomic mass number: N Z=A. The difference between the neutron number and the atomic number is known as the neutron excess: D = N – Z = A – 2Z.
中子数 原子序数等于原子质量数:N Z=A。中子数和原子序数之间的差异被称为中子过剩:D = N - Z = A - 2Z。
Neutron number is rarely written explicitly in nuclide symbol notation but appears as a subscript to the right of the element symbol. Nuclides with the same neutron number but a different proton number are called isotones.
中子数很少在核素符号表示时直接表示,但可以元素符号右侧下标的形式出现。中子数相同但质子数不同的核素称为同中子异荷素。
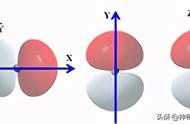
The atom’s chemical properties are determined by the number of protons and the number and arrangement of electrons. The configuration of these electrons follows the principles of quantum mechanics. The number of electrons in each element’s electron shells, particularly the outermost valence shell, is the primary factor determining its chemical bonding behavior. In the periodic table, the elements are listed to increase the atomic number Z.
原子的化学性质是由质子的数量、电子的数量和排列决定的。这些电子的配置遵循量子力学的原理。每个元素的电子壳层,特别是最外壳层的价电子层中的电子数是决定其化学键行为的主要因素。在元素周期表中,元素按原子序数Z的增序排列。
(待续)
,