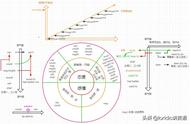
2.4 shall用于提供建议。
Shall I close the door?
我要不要关上门?
Shall we go swimming tomorrow?
我们明天要不要去游泳?
2.5 will用来表示请求
Will you tell me about the meeting?
你能不能跟我说一下会议的情况?
Would是will的过去式,但使用would表示请求时语气往往更加委婉。
Would you help me with the bag?
你能不能帮我拿一下包?
3.1 should用来提建议的程度或语气较为强烈。
It's very cold outside. You should wear more clothes.
外边很冷,你应该多穿点衣服。
You are sick. You shouldn't go to work today.
你生病了,就不要去上班了。
Which T-shirt should I wear? They both are cool.
我应该穿那件T恤衫,两件都很酷。

3.2 ought to和should的用法一样,也可以用来提建议。ought to比should更加正式,但并不常用,而且ought to不用于否定句或疑问句。
You ought to take your ID card with you every day.
你应该每天都带上你的身份证。
3.3 could用来提建议时的语气较弱,仅仅是提供了一种可能性或者解决某一问题的一个选项,这种建议并不是必要采取的。
A: I don't like my computer.
我不喜欢我的电脑。
B: Well, you could buy a new one!
那你就买台新的吧。
有时候,当我们使用could提建议的时候,会提供多个选项,并用or来连接。
If you like sports, you could play basketball or go swimming.
如果你喜欢运动,你可以打篮球,也可以游泳。
3.4 must也可以用来表达建议,而且其语气非常强烈。
You must pay attention to the instruction when you visit the museum.
你参观博物馆的时候必须注意说明。
按照建议语气的强烈程度可将上述语气助词从弱到强如下排序:
Could – Should - Ought to – Must
3.5 其他表示建议的表达方式:
If I were you, I would do sth. 如果我是你,我将会…
If I were you, I would buy the white shirt.
如果我是你的话,我会买这件白色的衬衫。
Had better do sth.
You had better take an umbrella.
你最好带上伞。

4.1在英语中,must和have to经常被用来谈论责任与义务。而must表示主观上的"必须",have to表示客观上的"必须"
I must have a rest.
我必须得休息一下了。
I have to go to work on Saturday to make up the time. I didn't work on Wednesday.
我必须在周六补个班,因为我周三没上班。
4.2 must not表示某事是"不被允许的",而don't have to则表示"不必要的或没有义务的"。
You must not touch the button without permission.
没有得到允许你不能碰这个按钮。
【在没有许可的情况下禁止做某事】
You don't have to work overtime today.
你今天不必加班。
【虽然没有义务,但也可以做某事】
4.3 表示"将来时"和"过去时"的责任与义务
无论是肯定还是否定,我们都只能用have to来形成"将来时"的责任与义务,即will have to(肯定)和will not have to(否定),"过去时"的责任与义务,即had to(肯定)和didn't have to(否定)。
5Logical deduction 逻辑减弱In the future, I think everyone will have to speak English.
我认为在将来每个人都必须说英语。
One day, I hope that I will not have to go to work.
我希望将来有一天我不必去工作。
Last year, I had to get up before 5 am to catch up the first bus to work.
去年的时候,我每天早上不得不在5点之前就起床,以便赶上第一趟公交去上班。
In the past, women didn't have to go to school.
在过去,妇女不必去上学。
这里所说的逻辑减弱是指在确定性上有所减弱,即某些事情变成了可能会发生。
5.1 might和could往往讨论事情得不确定性。
It might / could be raining today, so you should take an umbrella.
今天可能会下雨,所以带上伞吧。
【今天是否下雨不确定,只是有可能会下雨】
5.2 Might not和could not表示某事"可能不"发生。
Jack is very tired, so he might / could not come to the party.
Jack非常累,所以他有可能不会来参加party.
5.3 cannot或can't表示某事"不可能"发生。
Roc can't be in Beijing, I talked with him just now.
Roc不可能在北京,我刚刚还和他说话了。

5.4 对于"过去的事情"的推测
Must have done用于对过去的事情进行肯定推测,即"过去某事一定发生了"
Someone must have cleaned the room. It's very tidy.
房间非常整洁,一定是有人打扫过了。
Might / may / could have done用于对过去的事情进行不确定推测,即"过去某事可能发生了"
Someone must have cleaned the room. It might have been Roc.
一定是有人打扫过了房间。有可能是Roc。
Can't / couldn't have done用于对过去的事情进行否定推测,即"过去某事一定没发生过"
Someone must have cleaned the room. It can't have been Roc.
一定是有人打扫过了房间,但肯定不是Roc。
6.1 "现在"的可能性:might 动词原形
I can't recognize him. He might be Mr. Roc.
我认不出他了,有可能是Roc先生吧。
6.2 "过去"的可能性:might /may / could have done
My computer isn't working. It might / may / could have been out of juice.
我的电脑不能用了,可能是没有电了吧。
6.3 "将来"的可能性:might 动词原形 将来的时间
Roc might not go traveling next month.
下个月Roc有可能不会去旅游了。
到此,常用情态动词的用法就讲解完毕。我们在使用的过程中需要根据语气、程度以及时间的不同进行具体分析。
,