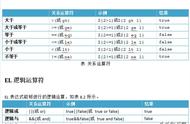
表达式 1?表达式 2:表达式 3 如果表达式 1 的值为真,返回表达式 2 的值,如果表达式 1 的值为假,返回表达式 3 的值。
示例: ${ 12 != 12 ? "表达式为真":" 表达式为假" }
“ . ”点运算 和 [] 中括号运算符.点运算,可以输出 Bean 对象中某个属性的值。 []中括号运算,可以输出有序集合中某个元素的值。 并且[]中括号运算,还可以输出 map 集合中 key 里含有特殊字符的 key 的值。
<body>
<%
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("a.a.a", "aaaValue");
map.put("b b b", "bbbValue");
map.put("c-c-c", "cccValue");
map.put("d", "dValue");
map.put("e", "eValue");
map.put("f", "fValue");
request.setAttribute("map", map);
%>
${ map['a.a.a'] } <br>
${ map["b b b"] } <br>
${ map['c-c-c'] } <br>
${ map.d } <br>
${ map.e} <br>
${ map.f} <br>
</body>
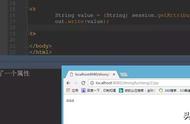
结果:

EL 个达式中 11 个隐含对象,是 EL 表达式中自己定义的,可以直接使用。

例子:
<body>
<%
request.setAttribute("aaa","aaaValue");
session.setAttribute("bbb","bbbValue");
%>
${requestScope["aaa"] }<br>
${sessionScope["bbb"]}<br>
</body>
结果:

pageScope --->pageContext 域
requestScope ---> Request 域
sessionScope ---> Session 域
applicationScope --->ServletContext 域
<body>
<%
pageContext.setAttribute("key1", "pageContext1");
pageContext.setAttribute("key2", "pageContext2");
request.setAttribute("key2", "request");
session.setAttribute("key2", "session");
application.setAttribute("key2", "application");
%>
${ applicationScope.key2 }
${ sessionScope.key2 }
${ requestScope.key2 }
</body>
结果: